If we want to do analysis properly on thermodynamic related things, we must devid the thing in three part. They are as below....
1. System
2. Surrounding
3. Boundary
1. System :
1. Close System
2. Open System
3. Isolated System.
1.1 Close System :
 |
| Closed System (a) |
 |
| Closed System (b) |
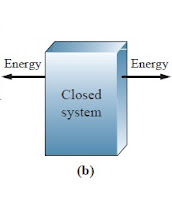
These are the examples of closed system of thermodynamics. fig (a) shows one testing tube in which hot water takes about 75 degree. and in that we knows that glass is good conductor of heat, so in that heat is transfer from water to glass. but the volume of water is constant in test tube. So (Heat) Energy transfer without transfer of mass. Fig (b) shows one plastic jar. also plastic is a good conductor of heat. In this case also (Heat) energy can transfer without transfer of mass.
1.2 Open System :
It is a system in which, both mass and energy may cross system boundary.
This fundamental diagram shows the property of open system. i.e. In this system energy as well as mass can cross boundary of system.
 |
| Open System (a) |
 |
| Open System (b) |
1.3 Isolated System :
It is a system in which, both mass and energy may not cross system boundary.
 |
| Isolated System (a) |
 |
| Isolated System (b) |
Fig (a) shows fundamental diagram of the property of open system. i.e. In this system energy as well as mass cannot cross boundary of system. Fig (b) shows perfectly insulated Thermos. Which is the perfect example of Isolated System. In this case mass as well as energy are not crossing the system boundry. Thus it is called as Isolated System.
2. Surrounding :
If we want to learn simply about surrounding, then remember one thing, "OUTSIDE THE SYSTEM IS SURROUNDING". But we have to remember one thing that surrounding also has one limited boundary.
Suppose we performing an experiment of boiling water in properly air-conditioned room. Then our system is water, and surrounding for this system is cool air. we cannot consider outside room air as a surrounding. So Surrounding itself has boundary.
3. Boundary :
Boundary is nothing but an imaginary line which separates system and surrounding. Boundary is always shown by dotted lines across system. Heat and mass can cross this line to do some useful work.
Or if you understand more about system surrounding boundary you can watch the video (link given below) to understand more about it.
Or if you understand more about system surrounding boundary you can watch the video (link given below) to understand more about it.
Thank You.


No comments:
Post a Comment